📝 Case Study: Investigating with Splunk
🔹 Overview
In this case study, I analyzed Windows + Sysmon logs in Splunk to uncover adversary techniques such as backdoor account creation, registry persistence, process execution, and obfuscated PowerShell activity.
Skills demonstrated:
- Querying logs with index searches & Event IDs
- Identifying backdoor accounts and persistence mechanisms
- Detecting malicious PowerShell and C2 callbacks
- Investigating anomalous user behavior and impersonation
- Decoding Base64-encoded payloads
🔍 Key Activities & Findings
1. Total Events in Index
- Queried logs with:
index="main" - Adjusted time range → All Time
- Found 12,256 total events ingested.
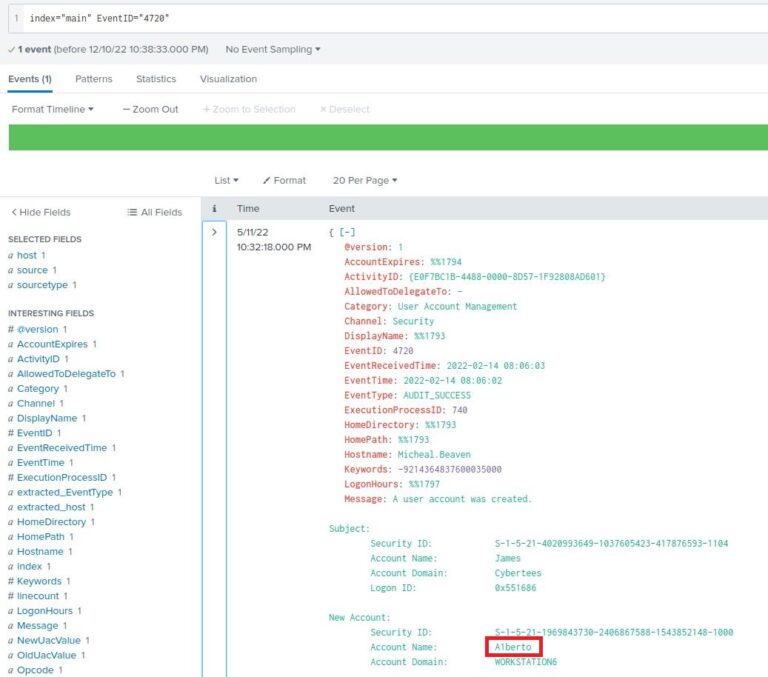
2. Backdoor User Creation
- Event ID 4720 → new user account creation.
- Search:
index="main" EventID=4720 - Found attacker-created account: A1berto
- Substitution trick: “L” replaced with “1” to mimic Alberto.
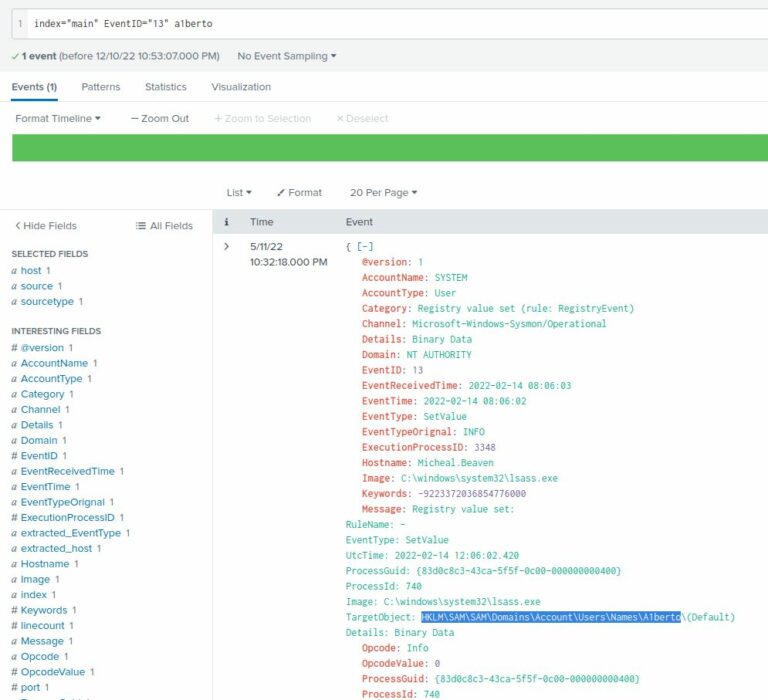
3. Registry Key Modification
- Event ID 13 → registry modification.
- Refined with username:
index="main" EventID=13 A1berto - Persistence established at:
HKLM\SAM\SAM\Domains\Account\Users\Names\A1berto
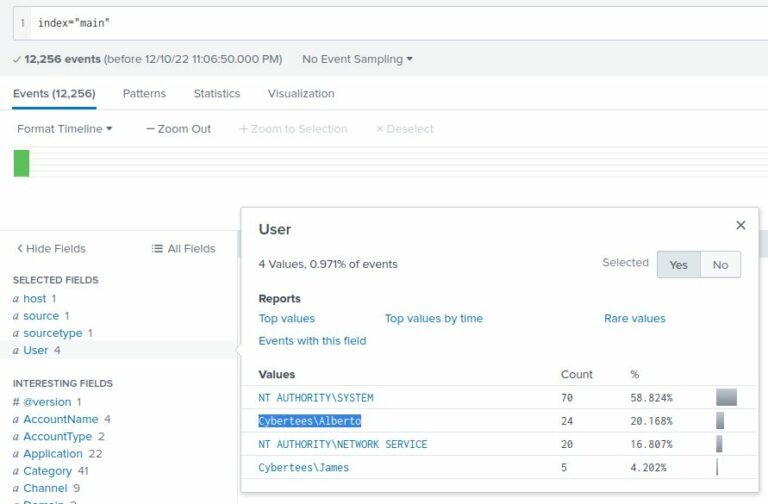
4. Impersonated User
- Analyzed user activity across logs.
- Adversary attempted to impersonate legitimate user: Alberto.
5. Remote Command Execution
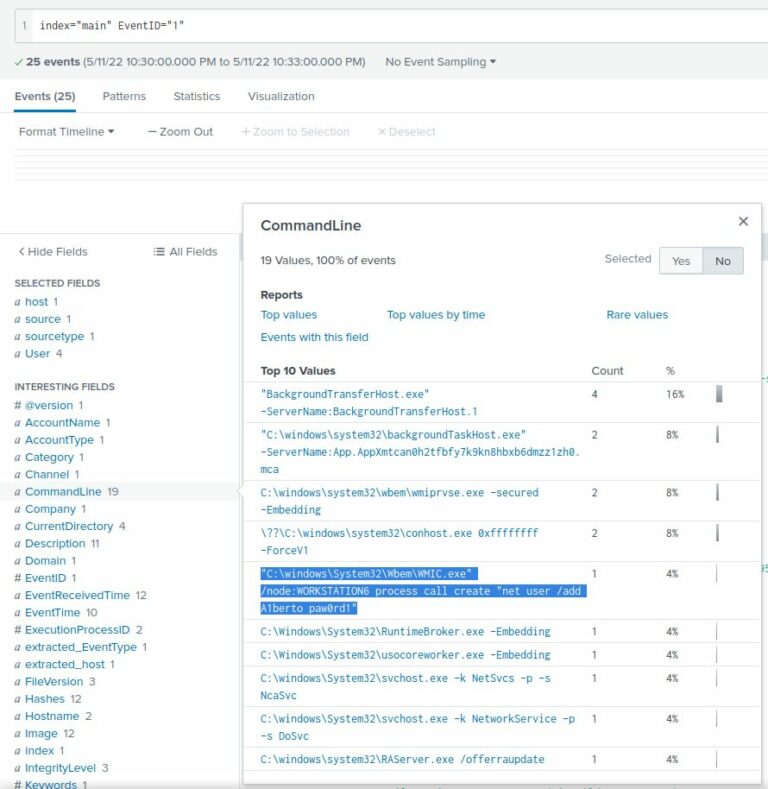
- Event ID 1 → process creation events.
- Identified WMIC command used for remote user creation:
“C:\windows\System32\Wbem\WMIC.exe” /node:WORKSTATION6 process call create “net user /add A1berto paw0rd1”
6. Backdoor Logons
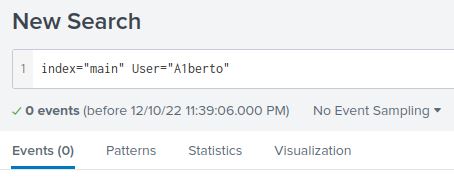
- Event ID 3 → network connections.
- Filter:
User="A1berto" - Result: 0 successful logons by the backdoor account.
7. Infected Host with PowerShell
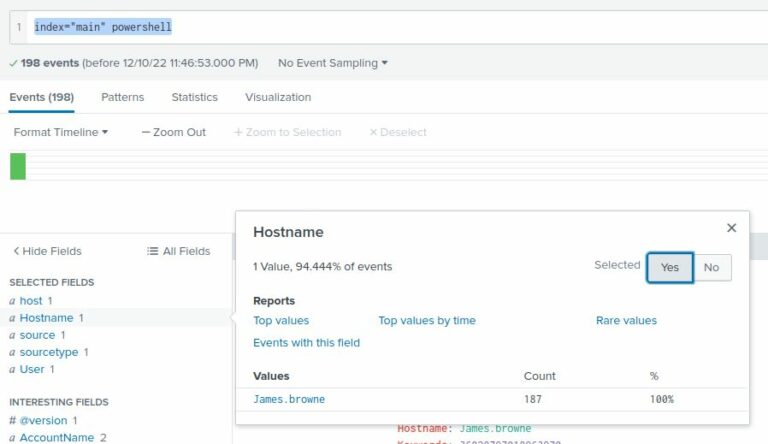
- Search:
index="main" powershell - Identified compromised host: James.browne
8. Malicious PowerShell Execution
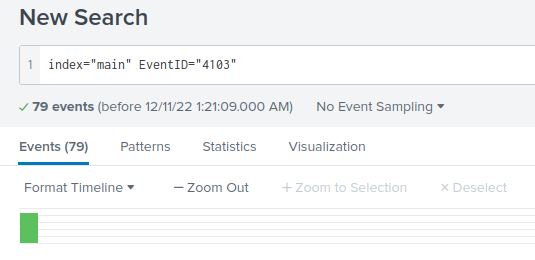
- Event ID 4103 → PowerShell command logging.
- Found 79 malicious PowerShell execution events.
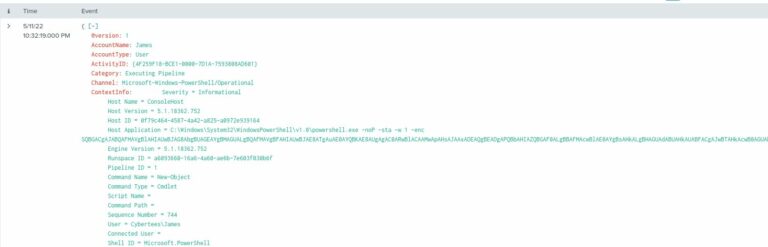
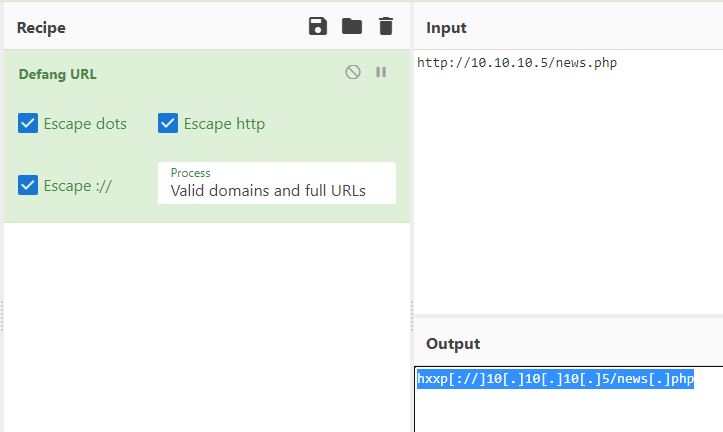
9. Web Request from Encoded Script
- Extracted encoded Base64 PowerShell payload.
- Decoded to reveal attacker C2 infrastructure:
hxxp[://]10[.]10[.]10[.]5/news[.]php
✅ Conclusion
This case study simulated a real-world intrusion chain, including:
- Persistence (backdoor account + registry key modification)
- Evasion (username masquerading)
- Execution (remote WMIC + PowerShell abuse)
- Command & Control (Base64-obfuscated HTTP request to attacker server)
By correlating Splunk searches, Event IDs, and log fields, I was able to reconstruct the adversary’s actions step by step.
This strengthened my skills in:
- SIEM-driven investigations
- Adversary emulation & detection engineering
- Practical log forensics in Windows environments
🔗 Navigation
- Back to SIEM Home